Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions worldwide. However, emerging literature is shedding light on a powerful ally in the battle against PD: strength training. Not only does this form of exercise improve physical strength and endurance, but it also holds the potential to make dopamine utilization more efficient, alleviate symptoms, and potentially slow down the progression of the disease. In this article, we delve into the benefits of strength training specifically tailored for PD, and explore ways to make this journey safe, enjoyable, and transformative.
Understanding the Benefits
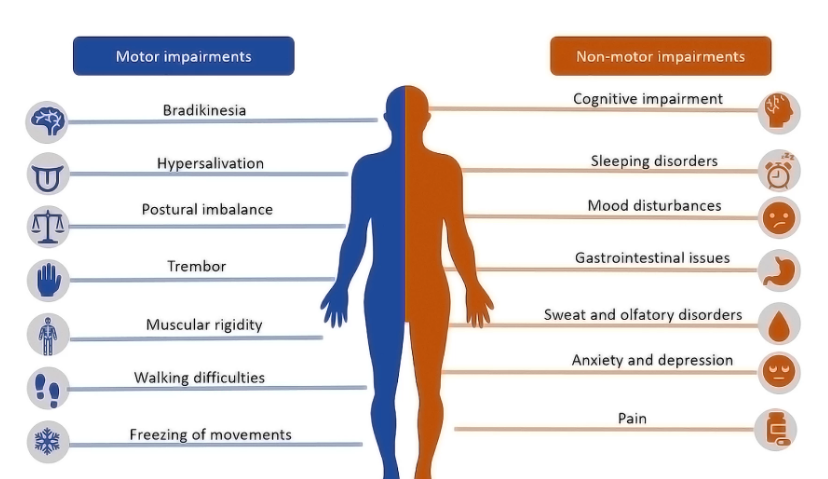
The advantages of strength training extend far beyond bulging biceps. Research has shown that individuals diagnosed with PD often experience a decline in gross muscular strength, particularly in areas like the back and hip extensors. This weakness can be attributed to the postural changes that commonly occur as the disease advances. The tendency to hunch shoulders and lean forward weakens postural muscles, compromising balance and increasing the risk of falls.
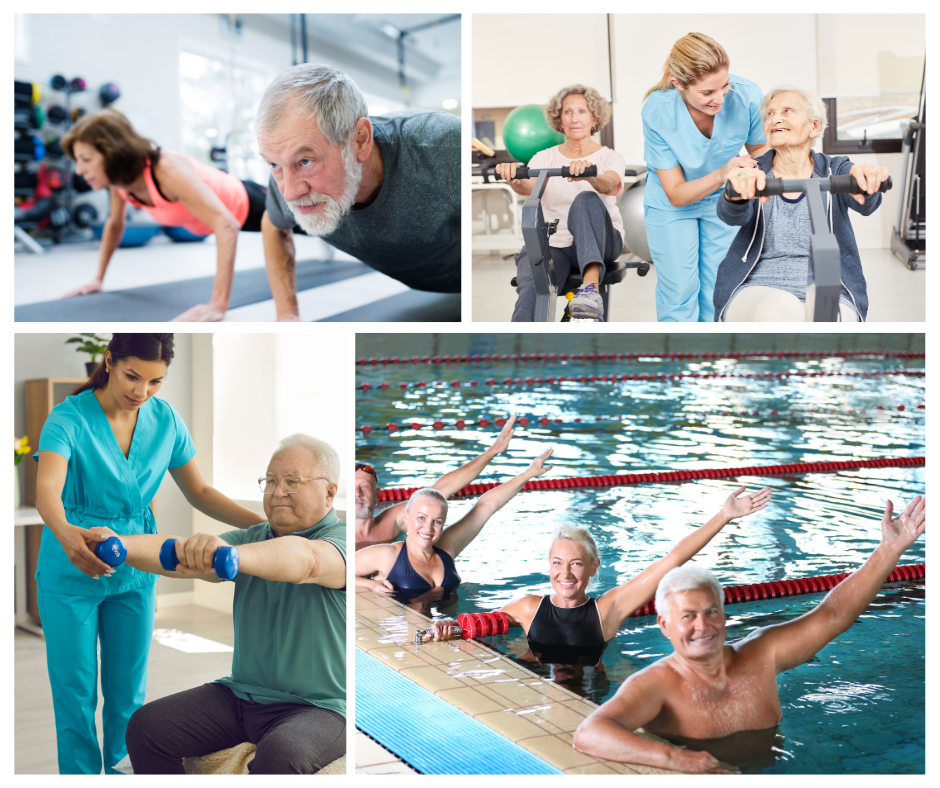
This is where strength training steps in as a formidable solution. By engaging in regular strength training exercises, individuals with PD can bolster their strength, stability, and confidence. The exercises not only counteract the muscular weakness associated with PD but also promote proper posture, thereby mitigating the risk of falls. Additionally, strength training helps improve dynamic balance and cognitive functioning, contributing to an overall enhanced quality of life.
Unveiling the Science
The science behind the efficacy of strength training for PD is multifaceted. One intriguing aspect is its impact on dopamine metabolism. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter critical for movement control, is often deficient in individuals with PD. Engaging in strength training appears to make dopamine utilization in the brain more efficient, potentially leading to a reduction in motor symptoms.
Moreover, strength training has been associated with anti-inflammatory effects, promoting a healthier neuroenvironment. It also facilitates increased brain connectivity, which can counteract the neural degeneration characteristic of PD. Among various types of exercise, weight training stands out as particularly beneficial for individuals with PD, thanks to its potential to address muscle weakness and posture imbalances.
 Embracing a Holistic Approach
Embracing a Holistic Approach
While strength training takes center stage, it’s important to recognize that a comprehensive exercise regimen can yield even greater benefits for those with PD. Incorporating a variety of exercises ensures a holistic approach to managing the disease. Resistance training, cycling, aqua aerobics, dance, and specialized programs like Rock Steady Boxing can all play a crucial role in maintaining physical and cognitive well-being.
Embarking on the Journey
For those considering adding strength training to their PD management plan, there are numerous avenues to explore. Personal training, guided by fitness professionals experienced in working with PD patients, offers tailored guidance and supervision. Physical therapy can provide targeted exercises to address specific needs, while group training environments foster camaraderie and motivation.
The key is to start gradually and progress at a pace that suits your individual abilities. Always consult with your healthcare provider before beginning any new exercise regimen, especially if you have existing health conditions.
Conclusion
The realm of exercise, particularly strength training, holds remarkable potential for individuals living with Parkinson’s disease. By actively engaging in regular strength training exercises, individuals can not only increase their physical strength and stability but also potentially enhance dopamine utilization, alleviate symptoms, and slow disease progression. It’s a journey that intertwines science, perseverance, and hope, promising a brighter horizon for those navigating the challenges of Parkinson’s disease.
Resources
Northwestern Medicine: Feinberg School of Medicine
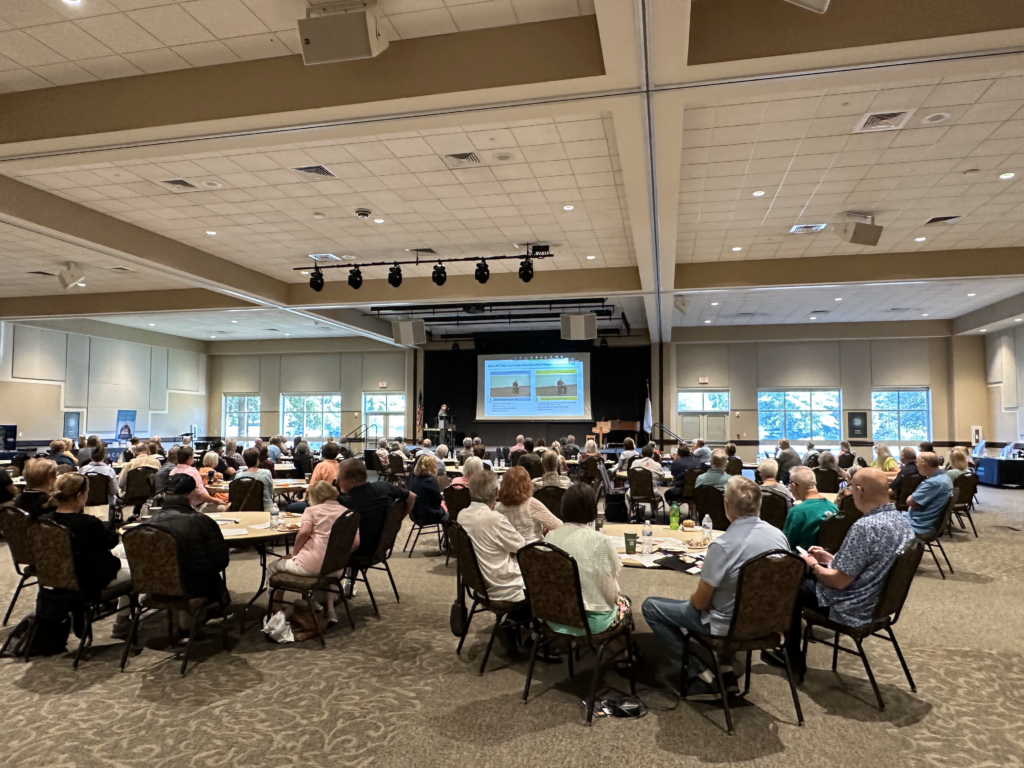
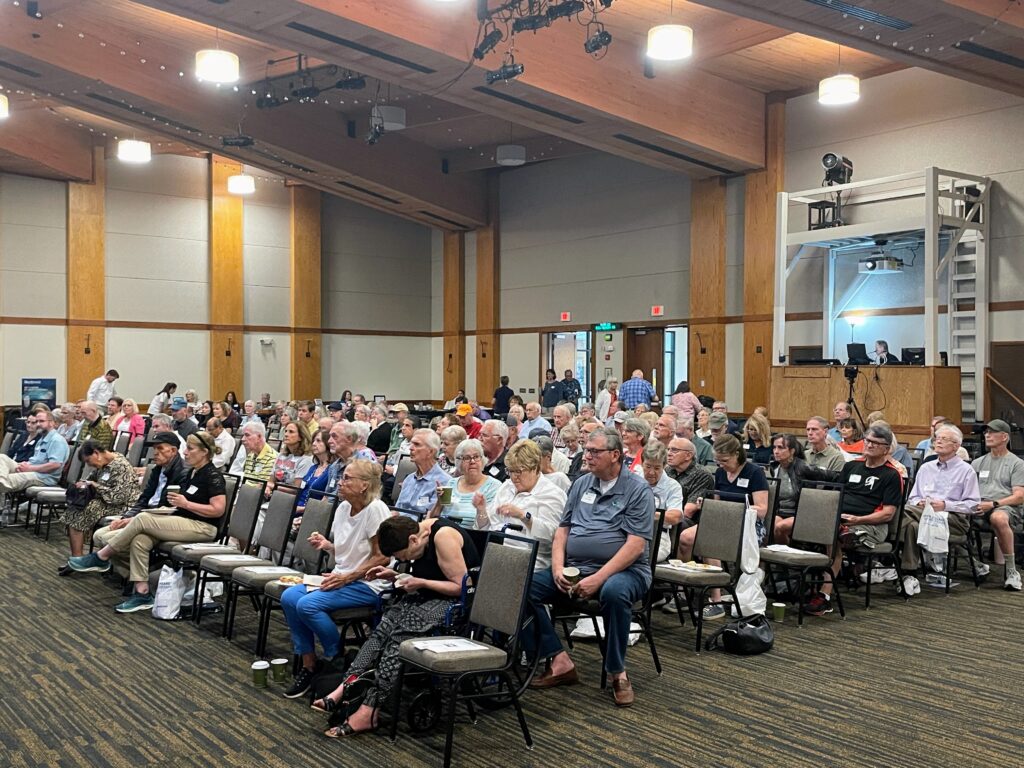
















 On Saturday, August 12 the Peterson Foundation for Parkinson’s welcomed nearly 150 members of the Middle Tennessee Parkinson’s community at the Gordon Jewish Community Center in Nashville for the Foundation’s 4th Annual Navigating the Parkinson’s Path, presented by Supernus. This day was a true testament to the power of community, bringing together individuals with Parkinson’s, caregivers, advocates, and experts.
On Saturday, August 12 the Peterson Foundation for Parkinson’s welcomed nearly 150 members of the Middle Tennessee Parkinson’s community at the Gordon Jewish Community Center in Nashville for the Foundation’s 4th Annual Navigating the Parkinson’s Path, presented by Supernus. This day was a true testament to the power of community, bringing together individuals with Parkinson’s, caregivers, advocates, and experts. Dr. Jill M. Giordano Farmer began the day by discussing a comprehensive approach to treatment as Parkinson’s progresses. Dr. Farmer stressed that nothing happens in isolation within the brain, making a mixture of medicines essential for a holistic approach. She also highlighted the significance of social engagement and exercise, which impacts both motor and non-motor components of Parkinson’s disease.
Dr. Jill M. Giordano Farmer began the day by discussing a comprehensive approach to treatment as Parkinson’s progresses. Dr. Farmer stressed that nothing happens in isolation within the brain, making a mixture of medicines essential for a holistic approach. She also highlighted the significance of social engagement and exercise, which impacts both motor and non-motor components of Parkinson’s disease. After a brief Rock Steady Boxing exercise break, facilitated by Colleen Bridges of Bridges for Parkinson’s, Dr. Thomas Davis provided valuable insights into disease modification and the role of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Disease-modifying therapies aim to slow the progression of Parkinson’s, providing hope for better long-term outcomes. Understanding alpha-synuclein and its contribution to the disease has led to new therapies and trials aimed at reducing its impact.
After a brief Rock Steady Boxing exercise break, facilitated by Colleen Bridges of Bridges for Parkinson’s, Dr. Thomas Davis provided valuable insights into disease modification and the role of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Disease-modifying therapies aim to slow the progression of Parkinson’s, providing hope for better long-term outcomes. Understanding alpha-synuclein and its contribution to the disease has led to new therapies and trials aimed at reducing its impact. The final presenter for the day was Dr. Daniel M. Corcos who shared the incredible benefits of resistance training, particularly its impact on individuals with Parkinson’s. While any form of exercise is beneficial, according to research studies weight training stands out as more advantageous, leading to a 7-point improvement in strength after a 24-month study. Additionally, resistance training enhances cognitive outcomes, preserves brain matter, and improves balance, posture, and gait.
The final presenter for the day was Dr. Daniel M. Corcos who shared the incredible benefits of resistance training, particularly its impact on individuals with Parkinson’s. While any form of exercise is beneficial, according to research studies weight training stands out as more advantageous, leading to a 7-point improvement in strength after a 24-month study. Additionally, resistance training enhances cognitive outcomes, preserves brain matter, and improves balance, posture, and gait.